What Causes Moles?
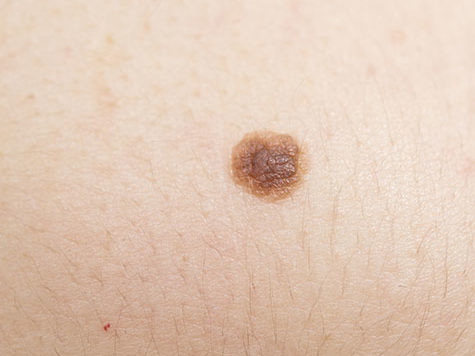
Moles occur when melanocytes, the cells that produce pigment in the skin, cluster together instead of evenly distributing pigment. This phenomenon can occur naturally and harmlessly or due to damage from ultraviolet (UV) light. Moles that result from sun damage may be more likely to turn into skin cancer. However, most moles are completely benign.
What Types of Moles Are There?
There are four basic types of moles.
- Congenital moles, or moles you are born with
- Acquired moles, or benign moles that occur after you are born
- Spitz nevi (moles), raised, pink, dome-shaped moles that typically appear before age 20
- Atypical moles, which are abnormal appearing and should be closely monitored for progression to melanoma
Atypical moles are not cancerous, but can sometimes mimic melanoma in appearance. If these moles have sufficient atypia, they are often removed as a precaution to prevent possible development into melanoma. Signs of atypia follow the same ABCDE guidelines for melanoma:
- Asymmetry
- Irregular or poorly defined Borders
- Uneven Color
- Diameter >6mm (the size of a pencil eraser)
- Evolution in shape, size, or color
Who Gets Moles?
Moles are extremely common, and nearly all adults have at least a few moles. Usually, these moles are either congenital or acquired moles. Often, moles will be more common in certain families as there is a strong genetic component to these skin lesions.
How Can I Prevent Moles?
Moles typically are not preventable. You may be born with moles or develop them as you age.
However, moles that result from UV damage can sometimes be prevented by avoiding excess sun exposure, wearing sunscreen regularly, and wearing UV protective clothing whenever possible. These sun-protective habits can protect your skin from melanoma and other serious skin conditions. In addition, they can help prevent the development of moles as well as signs of aging like sunspots.

Why Treat Moles?
If a mole is benign, you can still choose to have it removed. First, you may wish to have a mole removed for cosmetic reasons, particularly if it is large or in a very noticeable area. You may also choose to have a mole removed if it is irritating and rubs or catches on clothing or jewelry. Attempting to remove your mole at home should always be avoided, as you can cause unnecessary damage to your skin, infection, or scarring. Your dermatologist can safely and effectively remove a mole for you through a simple procedure.
How Can I Treat Moles?
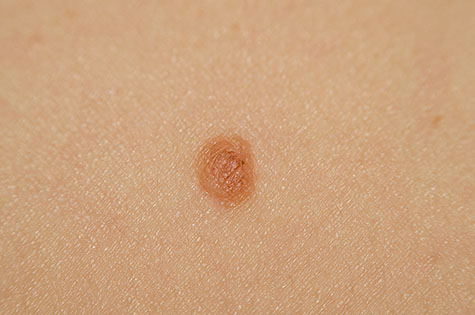
Moles are removed by surgical shaving or surgical excision. In either case, your dermatologist will numb the skin prior to the procedure. Your dermatologist may also recommend a shave removal test for atypical moles to ensure your health. More information on mole removal can be found here.
Schedule an Appointment
If you have a mole that is concerning you or you simply wish to have it safely removed, a dermatologist can help.
To schedule an appointment at Arlington Dermatology, please call our office or contact us online.
Mole FAQs
What is the fastest way to get rid of moles?
Your dermatologist can remove a mole via shave removal during an office visit or with a surgical excision. These are both safe and low risk procedures.
Should I get moles removed?
Moles can be cosmetically unsightly, irritating, or suspicious for skin cancer. Whether you wish to have a mole removed for cosmetic or medical reasons, the experienced, board-certified dermatologists at Arlington Dermatology can safely remove your mole where possible.
When should you get moles checked?
If a mole appears suspicious, it is important to have your dermatologist evaluate it. Signs to look out for include asymmetry, irregular borders, uneven color, large diameter (>6 mm), or new changes in appearance. In addition, it is beneficial to schedule full body skin exams with your dermatologist to routinely monitor your body for any atypical lesions.
How can I tell if a mole needs to be examined?
If you are concerned that your mole may be unhealthy, monitor for changes in shape, size, or color. New moles may also be concerning if they appear beyond young adulthood.
How long do you have to wear a bandage after mole removal?
It is advised to keep a bandage at the site of the mole for about 24 hours, then you can remove the bandage and wash the site with gentle soap and water to keep the area clean. It is recommended to apply vaseline and a band-aid to the wound site daily until the site has healed in ~7-14 days typically.
Could my mole be cancerous?
If your dermatologist has concerns regarding your mole, he or she may send the excised tissue to a laboratory to be examined under a microscope for further evaluation.
Can moles be removed from face without scarring?
It is not possible to remove moles from the skin without creating some type of scar. The extent of scarring depends on how your body specifically heals, as well as the depth and size of the mole. Moles can be removed by surgical excision or shave removal. In either case, your mole will be carefully separated from the surrounding skin to ensure minimal scarring and avoid complications.
What causes moles?
When cells in the skin (melanocytes) grow in clusters, moles are formed. New moles can sometimes emerge as an individual’s body ages or undergoes certain changes (ex: pregnancy).
How does mole removal work?
Moles can be removed by surgical excision or shave removal. Your dermatologist will numb up the area with an injectable anesthetic to make sure you are comfortable prior to the procedure. Then, the mole will be removed either by surgical excision (using stitches to close the wound) or shave removal.
Can you remove a mole at home?
Attempting to remove your mole at home should always be avoided, as you can cause unnecessary damage to your skin, infection, or scarring. Furthermore, it is important to know if a mole is concerning for your overall health or not before removing it. Your dermatologist can examine a mole to make sure it is healthy and normal, as well as safely remove a mole for you through a simple in-office procedure.



