What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma?
The primary cause of basal cell carcinoma is ultraviolet (UV) light exposure. This can be from either excess exposure to natural sunlight or tanning beds. UV damage ultimately results in mutations to the DNA of skin cells, resulting in skin cancer.
Who Gets Basal Cell Carcinoma?
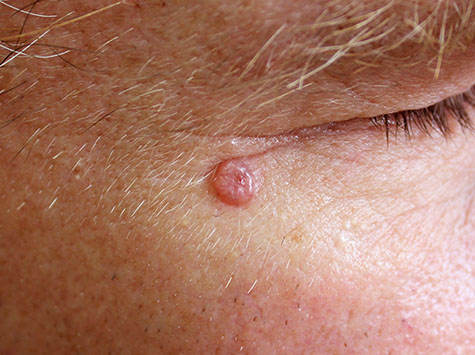
Basal cell carcinoma can affect anyone, however, you are at a higher risk if you fall into the following categories:
- Fair skin
- Blond or red hair
- Skin that freckles easily
- Light-colored eyes
- Live in a sunny climate
- Weakened immune system (medication-induced or medical condition)
- Spend a significant amount of time outdoors
- History of sunburns, especially to the point of blistering
- Certain genetic conditions (ex. Basal cell nevus syndrome)
How Can I Prevent Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Protecting your skin from the sun is just one way to prevent basal cell carcinoma. In addition to avoiding prolonged sun exposure, you should wear sun-protective clothing and SPF 30 or higher sunscreen regularly to protect yourself from damaging UV exposure. It is also important to perform routine skin checks at home and be able to recognize the signs of basal cell carcinoma or other types of skin cancer. If you notice any suspicious signs or symptoms of basal cell carcinoma, schedule an appointment with a board-certified dermatologist for a professional evaluation.
tent
Enter Shortcode:

Why Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma?
It is important to promptly treat basal cell carcinoma to prevent further spread of the cancer and potential possible severe effects to one’s overall health. Basal cell carcinoma is usually treatable, especially when diagnosed at early stages, but can be more difficult to treat with progression and time. For this reason, it is important to perform regular self-examinations and to consult a board-certified dermatologist if a concerning lesion is found.
How Can I Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma?
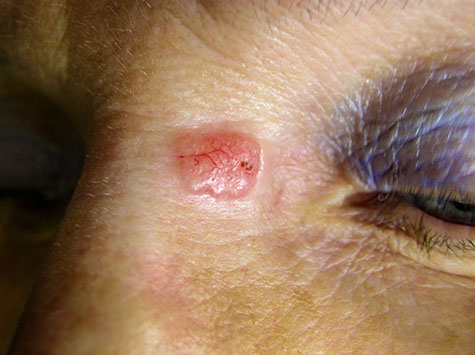
First, your dermatologist will make a formal diagnosis through a careful visual examination and likely a skin biopsy. After diagnosing basal cell carcinoma, the cancerous skin cells can be effectively treated by one of several treatment options including:
- Excision
- Mohs surgery
- Curettage
- Topical 5-flourouracil or imiquimod
Schedule an Appointment
If you notice signs of basal cell carcinoma, you should have your concerns professionally evaluated by a qualified, board-certified dermatologist as soon as possible.
To schedule an appointment at Arlington Dermatology, please call our office or contact us online.


